Spiders weave catapultlike mechanisms into their webs to hoist
Are you fascinated by the sticky properties of spider silk and the intricate designs of spider webs? In this video, we'll be using a microscope to observe a.

Picture of the Week Spider Web Through a Microscope Lens
Probably the most readily recognizable form of spider web is the orb web. It was once thought to be the pinnacle of spider web evolution. New molecular evidence has nonetheless suggested two alternative scenarios (Bond et al. 2014; Fernández et al. 2014): (1) that the orb web evolved earlier than originally postulated and may represent the ancestral form of all spider webs, or (2) the orb web.
Smithsonian Insider Drugged spiders’ web spinning may hold keys to
Activity: Viewing a Spider Web. A compound microscope like THIS or any of THESE . Find a complete, dry spider web. Observe the web for patterns. Different types of spiders use different types of construction techniques. Sketch your builder's style. Take note of the spider on the web (if it is still there).

A Spider Web Under the Microscope Requirements, Procedure, Observation
Remove any excess spider web. Cover the slide using a cover slip, pressing it down gently. Place the slide on the microscope for observation. ** If nail polish is not available, then a slide mounting fluid may be used to attach the spider web on to the slide. Spider Web captured by Steve Gibson from Publicdomainpictures.net.
Zoonomian A Web of Intrigue
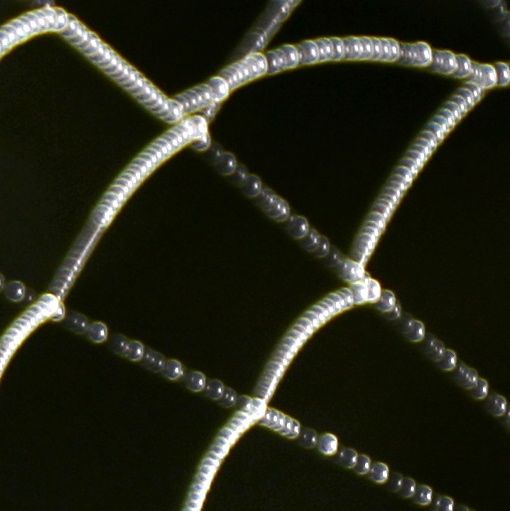
Optical effects on spider webs The html formatting and custom instructions have been disabled on this server.. (Araneus diadematus) under the microscope and determined the diameter of the sticky drops as 25 μm approximately, estimating that of the thread in between as one tenth of that, i.e. 2-3 μm. There were 12 to 13 drops per.
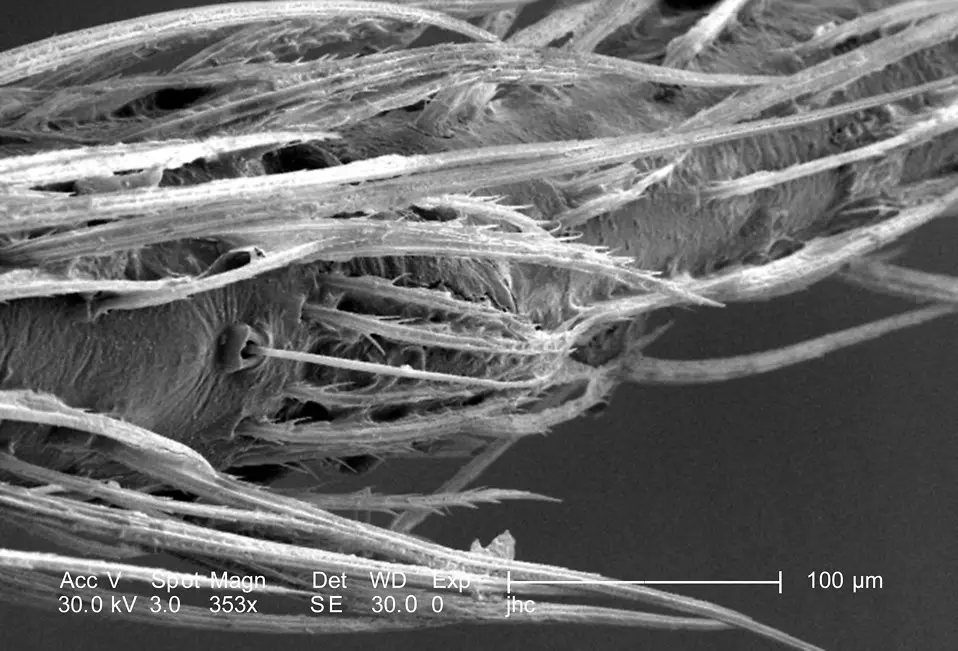

A Spider Web Under the Microscope Requirements, Procedure, Observation
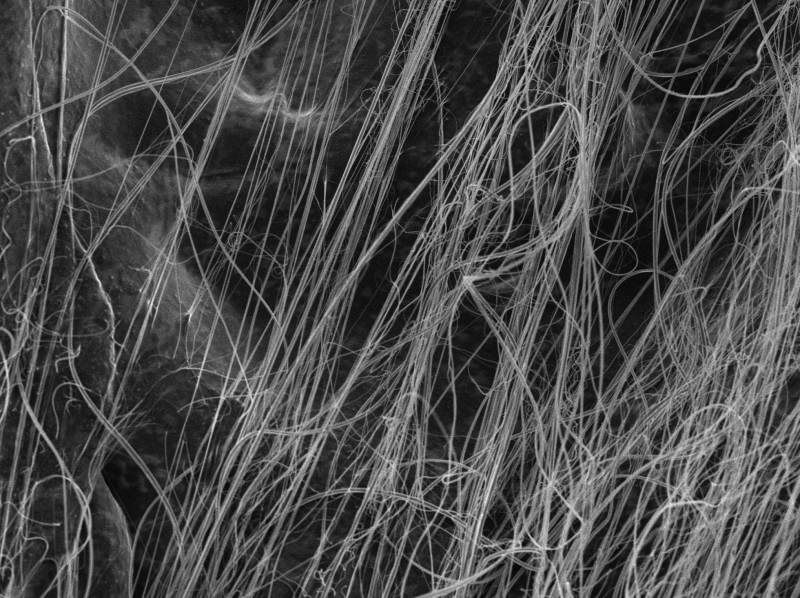
For example, a spider under a microscope looks like an alien (you can see a photo of its eyes above). At magnification of several dozen, you can observe fur on its body, and at 1000x magnification you can examine its jaws and the small claws on its legs.. It is especially interesting to observe a spider eating or weaving a web. It is easy to.

Spider Silk Gland Spigots (gasteracantha Sp.) Photograph by Dennis
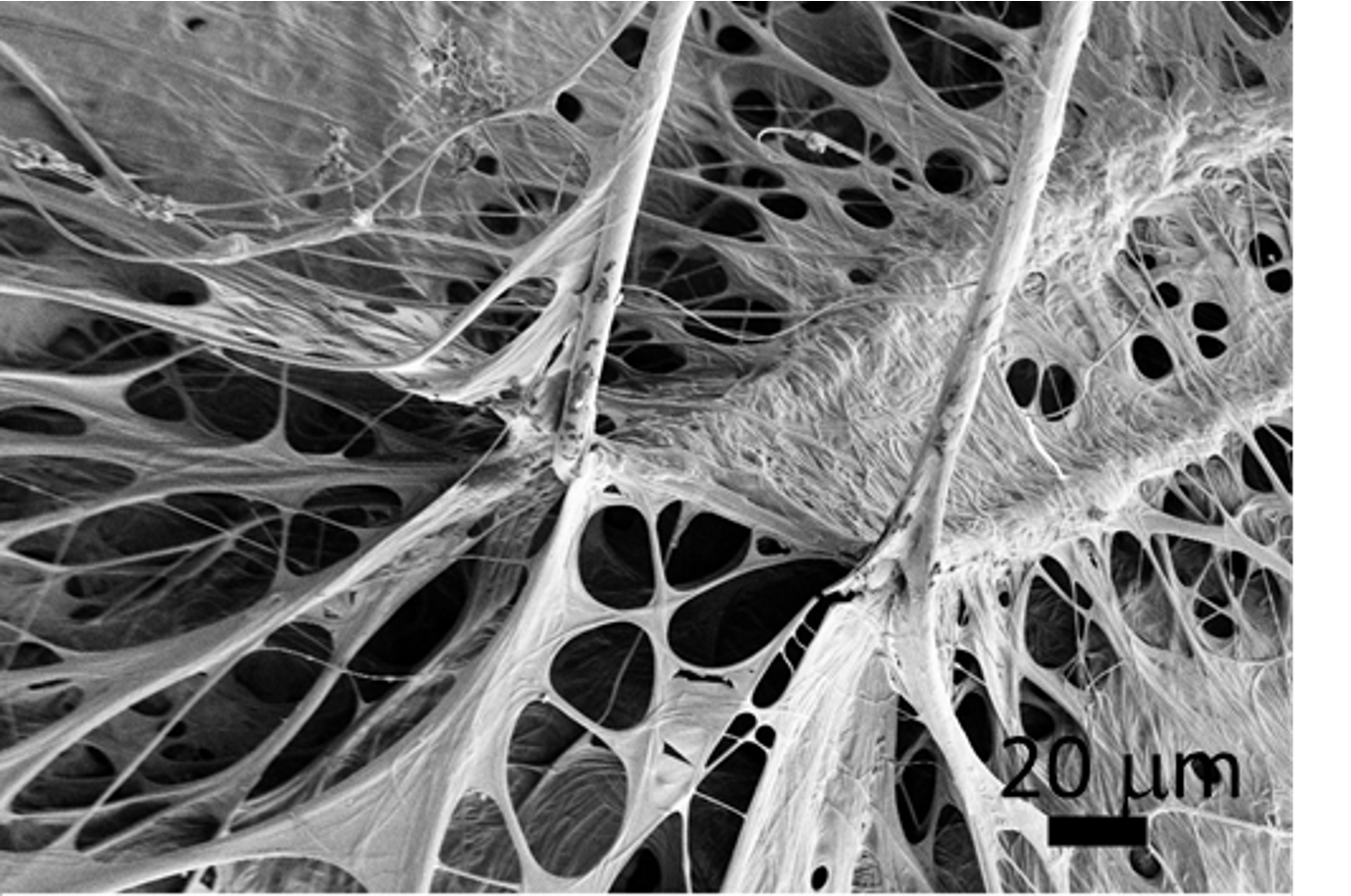
2.1. Spider web construction. The spider built its web in a rectangular frame over a few days (figure 1a).Spiders build webs in low lit environments, often using branches, rocks and corners as support [].To build intact spider webs in controlled conditions, we built a rectangular 35.6 × 35.6 × 24.4 cm frame (figure 1a), adapted from the Spider Web Frame (SWF) method developed by STS [].

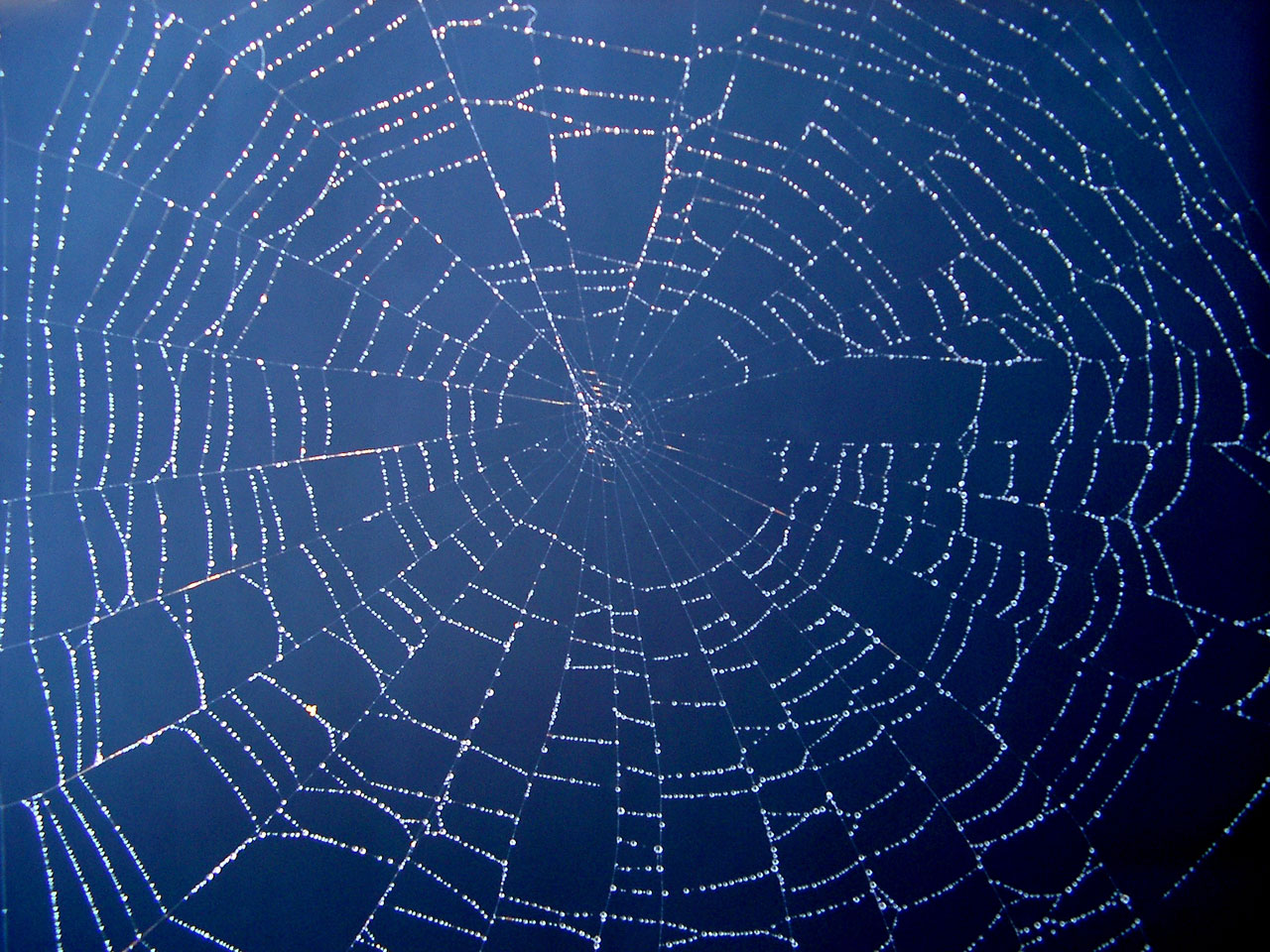
FileSpider web with dew drops04.jpg Wikimedia Commons
Here are some of the common uses of spider webs under a microscope. 1. As a Trap: One of the most common uses of spider webs is as a trap to catch prey. The sticky threads of the web are specifically designed to trap insects and other small animals that the spider can feed on.

Electron Microscopy Images; Spider / A domestic spider found in shower
Spider web is made of very thin silk. Spiders make this web to catch prey that gets caught when flying or passing through this web. When caught, the spider w.

Spider Web Under the Microscope
A spider web, spiderweb, spider's web, or cobweb. The figure on the left is an optical microscope image of glue balls. The second figure from left is a scanning ion secondary electron image of the glue balls.. Its microstructure is under investigation for potential applications in industry, including bullet-proof vests and artificial tendons.

Giant Spider Webs Appear In Dallas Suburb Of Rowlett Immortal News
Transmitted Off Crossed Circular Polarized Light Definition/Function: Significance in the Environment: Characteristic Features: Associated Particles:

Free Images nature, animal, wildlife, biology, predator, fauna
the physics behind cell structures. The physics at work in the beading of dewdrops on a spiderweb is the same as that which drives the sub-microscopic beading of a protein called TPX2, which is necessary to building microtubules (the skeleton of the cell) and which also plays a role in some cancers. As any cook knows, some liquids mix well with.

Best Beginner Microscope Experiments of 2018 for Hobbyists and Kids
But I saved the most spectacular part of the spiders leg for last. The foot of a spider is a very interesting object to study under the microscope. You can see how the garden-spider is able to cling to the threads of its web. The foot possesses two claws, one downward pointing hook and several serated hairs.

Spider Web Under the Microscope
Biophysicists at Johns Hopkins University have discovered one of the keys to the super-elasticity of spiders' webs,. Ha's team helped translate what was seen under the microscope into measurements of force. The team wasn't expecting the spider silk inserts to show such linear behavior because, according to Ha, they don't form well-defined.

Spider's web, SEM Stock Image Z430/0434 Science Photo Library
Here, fluorescence microscopy shows TPX2 (green) transitioning from a uniform coating on a microtubule (not shown) into discrete beads. Scale bar 1 micron, timestamp in seconds.

' Ribbonthreads' in the webs of brown spiders (Loxosceles spp)
The amazing behaviour of the spider web was witnessed under high humidity environment (Boutry and Blackledge, 2013, Savage et al.,. (SEM) was performed by JEOL scanning electron microscope (JSM-6610LV) to determine the microstructure of the different major components of the web. For nanoindentaion test,.